Before You Buy Moringa Oleifera Tree Products
WARNING: Beware of Moringa oleifera tree bad cultivation or manufacturing practices when you buy products. Take a good look at this report (Feb – 2015) video report – supplement bad practices in major USA shops
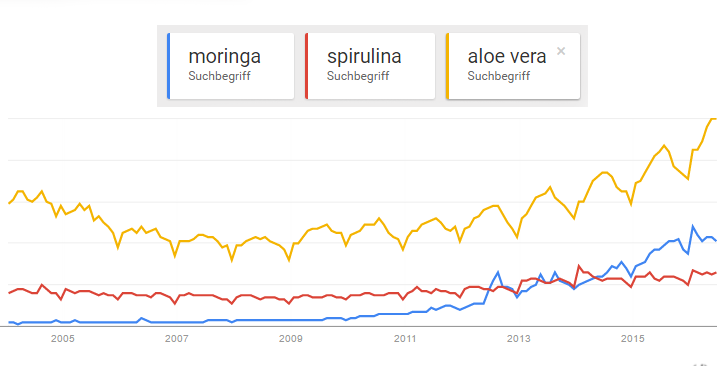
The flow of Moringa oleifera products onto the market is skyrocketing. Moringa, a practically unknown plant a few years ago, is now more trendy than many other popular plants. Take a look at Moringa trend evolution from 2007 till now. Impressive don´t you think? Blueberries will be soon in its rear-view mirror, Aloe Vera next 🙂
Although it is good that more people became aware of Moringa tree benefits, it’s fame brings bad things along.
The market place has plenty of low-quality Moringa oleifera manufactures attempting to capitalize on unsuspecting and uneducated consumers. A large amount of Moringa oleifera products on the market are made from cheap Moringa with a lack of product quality control. While these products may be affordable, they may not be as the label says.
Moringa oleifera nutrients could also easily be lost in the manufacturing process and, or amount of time the product takes, to go from a living plant into your hands.
For example, Moringa oil could be faked, not the real stuff or be mixed with other oils. Therefore buyer beware. Moringa oil is 20 times the cost of vegetable oil so the motivation is definitely there for diluting the oil with something cheaper.
Remember that the point of buying Moringa oleifera tree products is the incredible amount of nutrients and properties it contains, not just to buy green powerless powder compressed into capsules with a nice name on it. Therefore beware from whom and where you buy Moringa products.
To do list before you buy Moringa oleifera products
° Make sure that you buy products containing 100% Moringa oleifera.
° Verify that the Moringa oleifera products comes in a vegetarian or vegan capsule.
° Make sure you do your due diligence on the manufacturer and where they source their Moringa oleifera products from.
° Make sure the Moringa oleifera tree supplement that you buy (Moringa powder, capsules…), are the freshest possible. The longer Moringa oleifera powder stays in a warehouse or the Moringa capsules in shop shelves, the more nutrients are lost. Loss of up to 50% of vitamins can be reached after six months of storage.
° Identify what process is used to dry the Moringa oleifera leaves. Many farmers, producers of Moringa oleifera powder don´t care how they dry the Moringa leaves. See study on effect of dehydration on the nutritive value of Moringa oleifera tree leaves Moringa Sun dried – VS – Shadow dried – VS – Oven dried
° Before you leap in to buying Moringa oleifera products, ensure the products you buy are of the highest quality, and not mixed with any additives and fillers. The supplier should be intimately involved in the harvesting, cleaning, and production process to ensure the Moringa oleifera products you buy, are of a high standard.
After You Buy Moringa Oleifera Tree Products
Moringa oleifera leaf products should be stored in air-tight containers protected from heat, humidity and light. Moringa trees may like lots of sun but the sunlight is not good for the Moringa oleifera products.
If you buy Moringa tea, don´t forget that what’s inside the bag is very nutritious. After drinking your tea, open up the bag and use the powder in it for a milkshake, salad or any other dish. Other possibility is to feed your pets with it. Mix your pet food with the Moringa tea bag powder.
Don’t Like The Moringa Taste? Neutralize It!
To enjoy a delicious Moringa drink, simply take half a teaspoon of Moringa powder, add a teaspoon of honey, squeeze a little of lemon, mix them together and add water.
You can also drop a spoon of Moringa into your soup after cooking. Just enough Moringa not to spoil the original soup taste! Use your own imagination to neutralize the Moringa taste!
When you buy Moringa powder, 6g of powder is a good goal to eat per day. Start with much less though unless you want to cleanse your system! A teaspoon is around 2 or 3 grams of moringa leaf powder. It roughly equates to 6 Moringa capsules. How to use Moringa
After Buying Moringa, How To Use Moringa Oleifera Tree Products
The Moringa oleifera leaf, fresh or processed into dried powder, can be used as an every-day food item in a multitude of ways: in ready-made meals, juices, breads, pasta, fritters, condiments, instant soups, etc. Food made with Moringa products can be used in households, school cafeterias, dispensaries, maternity wards, nutrition rehabilitation centers, as well as in restaurants and supermarkets.
1. The nutritional content of fresh Moringa oleifera tree leaves
Eating 100 grams fresh Moringa oleifera tree leaves provides you with as much protein as an egg, as much calcium as a big glass of milk, as much iron as a 200 grams beef steak, as much vitamin A as a carrot and as much vitamin C as an orange.
Indeed, 100 grams fresh Moringa oleifera leaves are enough to cover
° 30 to 100% of the daily recommended intake of calcium (30 to 50% for teenagers, 40 to 60% for adults, children and pregnant and breastfeeding women, 80 to 100% for young children below 3 years old)
° 25 to 80% of the daily recommended intake of iron (25% for pregnant women, 40-60% for teenagers and women, 50 to 100% for men and children).
° As for vitamins, the recommended daily intake for vitamin A varies from 400 μg retinol equivalents (young children) to 1,000 μg retinol equivalents (breastfeeding women).
Therefore, 100 grams of fresh Moringa oleifera tree leaves could theoretically cover 100% of daily needs, but this is highly variable depending on storage conditions and how they are eaten, as vitamin A degrades over time and when exposed to light or heat. Similarly, 100 grams of fresh Moringa oleifera leaves could cover 100% of the vitamin C requirements, for which the recommended daily intake varies from 60 mg (young children) to 130 mg (breastfeeding women), but this vitamin degrades quickly with time and during cooking.
° For optimal nutrient retention, it is advised to consume fresh Moringa oleifera tree leaves shortly after harvesting and to cook the leaves for a short time (a few minutes only), or even to eat them raw if they are young and tender
2. The nutritional content of dry Moringa oleifera tree leaf powder
Another way of consuming Moringa leaves is to dry them and reduce them into powder, making it easier to store and use at any time. To ensure the good nutritional and microbiological quality of the leaf powder, its water content has to be lower than 7%, the drying time should be as short as possible and the drying temperature not too high (no more than 50-55°C).
Even if a large amount of the vitamins are lost during drying and storage, the leaf powder still constitutes a very rich nutritional supplement, since it is a concentrate of the Moringa oleifera leaves.
Moringa tree leaf powder can be stored for some time before it is consumed. If so, the leaf powder has to be stored in a water- air- and light-proof container to preserve as much vitamins as possible and avoid microbial contamination. In storage, the protein and mineral contents will be preserved for up to six months or more, whereas a loss of up to 50% of vitamins can be reached after six months of storage.
Once the container is opened, the leaf powder should be consumed quickly (within one week) since its water content will increase and it will be exposed to microbial contamination. For this reason, it is advised to package Moringa oleifera leaf powder in rather small containers.
3. The nutritional content of cooked Moringa oleifera leaves
Fresh Moringa oleifera leaves can be eaten raw, if they are very young and tender, but usually they are cooked. Even if cooking the leaves destroys a part of their nutrients, notably vitamins, others become easier to assimilate. For this reason, it is important to consider various ways of cooking the leaves and to understand how to preserve the maximum amount of nutrients. This can be achieved by associating Moringa oleifera tree leaves with other ingredients that enhance the availability of nutrients, by cooking the leaves only for a short time, or by keeping the liquid (water, sauce) in which the Moringa oleifera leaves are cooked. Using Moringa oleifera leaf powder is also a way of preserving nutrients (although some have been lost during drying and storage), as the powder can be added to food after cooking.
Moringa oleifera tree leaf powder per day cover
Moringa Calcium – 10g
° About 30% of the recommended daily intake for children between 1 and 3 years old.
° About 25% of the recommended daily intake for children between 4 and 9 years old as well as adult women.
° About 15% of the recommended daily intake for teenagers and women over 55.
Moringa Iron – 10g
° About 30% of the recommended daily intake for children between 1 and 12 years old.
° About 15% of the daily recommended intake for teenagers.
° About 20% of the daily recommended intake for adults over 55.
° About 12% of the recommended daily intake for adult women.
° About 7% of the recommended daily intake for pregnant women.
Moringa Vitamin A – 10g
° 50 to 100% of the recommended daily intake for all population categories.
Moringa Vitamin C
A study from Sri Lanka showed that on average, leafy vegetables lose 32% of their vitamin C content when they are boiled for five minutes, and 54% in ten minutes. Steaming is less damaging, with 15% loss in five minutes and 39% loss in ten minutes. Cooking Moringa oleifera tree leaves or Moringa oleifera tree leaf powder the least possible time is thus a good way to preserve the vitamin C content.
Moringa Beta-carotene 10g
The World Vegetable Centre (AVRDC, Taiwan) showed that the retention of total carotene and beta-carotene of Moringa oleifera tree leaves was enhanced by adding oil to the leaves during pressure cooking (76-99% of retention with oil against 46-63% without).
The bioavailability of Moringa plant nutrients
The bioavailability of nutrients is the ability they have to be digested and used by the human body. The bioavailability of the iron provided by plants is lower than when provided by meat. A good way to improve the availability of iron to the body is to add vitamin C to the dish. This can be done by using lemon juice, lemon peel or fresh tomatoes.
AVRDC demonstrated that boiling Moringa tree leaves in water enhanced the in vitro iron bioavailability of fresh leaves and leaves dried powder by 3.5 and 3 times, respectively. In addition, boiling the leaves in water enhanced aqueous antioxidant activity. This shows that cooking Moringa oleifera tree leaves does not necessarily have a negative impact on nutrient intake. The heat destroys some of the vitamin C, but improves the assimilation of iron. The best option is to vary consumption modes.
4. Moringa oleifera – water soluble and fat soluble vitamins
Vitamin C and all the B vitamins contained in the Moringa oleifera tree leaf are water-soluble. Other vitamins are soluble in fat: such is the case of vitamin A (ß-carotene) and E (a-tocopherol). When cooking fresh or dried leaves, the cooking water should be kept to benefit from the vitamins B and C, soluble in water. In addition, to render the fat-soluble vitamins A and E available, it is suggested that the leaves be cooked using oil or other sources of fat. Ideally, the Moringa leaves should be quickly boiled in a small quantity of water. Add both Moringa oleifera tree leaves and the cooking water to a sauce containing a source of fat. This way both water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins, only slightly diminished by cooking, are made available.
How to eat Moringa leaf powder?
Moringa leaf powder can be added to just about anything you eat. It is extremely versatile.
It takes roughly seven pounds of fresh Moringa leaves, to make one pound of Moringa leaf powder. 7 lbs. fresh = 1 lb. ground and dried. Some people eat between 1 teaspoon and 1 tablespoon daily, others eat a lot more than that.
Moringa leaves make a very “potent” powder, we recommend that you go slowly when eating it. Start out with eating a small amount, and increase it daily.
Moringa leaves can be eaten fresh, cooked or dried

You eat Moringa leaves, as you eat any other vegetables.
To keep the nutrition, add Moringa leaves, right near the end of cooking time for all dishes.
Benefits of Eating Moringa Leaves
Moringa leaves, are a welcome addition to any diet, whether in its fresh state or dried and ground into powder.
How much moringa should I use and eat? How to use and eat moringa?
How to eat Moringa leaves
You can eat moringa leaves in all sorts of ways: Moringa leaves can be eaten in salads, added to rice or pasta or any other dish. The list is endless. Juice the Moringa leaves, fry or steam the leaves in any meal, bake Moringa in goodies, add to shakes and baby milk… use your imagination!
Moringa leaf powder can be used as a tea, added to beverages, sprinkled on food or taken in capsules. It can be used in soups or any other dish
There are a thousand and one ways to eat Moringa. Let’s start with moringa salad. Cut the fresh Moringa leaves with their stalks, wash with water(add salt to it). Remove from the stalk. Add other salad ingredients like cucumbers, cabbage, carrots, etc. Add moringa oil and you are good to go…
Attention: Excess heat destroys some of the vitamins, and all of the enzymes of Moringa leaves or Moringa powder. Never cook the fresh Moringa leaves or powder for too long! This is the rule of thumb on eating moringa leaves or powder for any dish.
How much Moringa leaves should you use, eat?
Wondering how much Moringa to take or how much Moringa per day? 100 grams of fresh Moringa leaves will bring twice as much nutritive material as 100 grams of most other vegetables.
Eating 100 grams fresh Moringa oleifera leaves provides you with as much protein as an egg, as much calcium as a big glass of milk, as much iron as a 200 grams beef steak, as much vitamin A as a carrot and as much vitamin C as an orange.
100 grams of fresh Moringa leaves could theoretically cover 100% of daily needs, but this is highly variable depending on storage conditions and how they are eaten, as vitamin A degrades over time and when exposed to light or heat. Similarly, 100 grams of fresh Moringa oleifera leaves could cover 100% of the vitamin C requirements, for which the recommended daily intake varies from 60 mg (young children) to 130 mg (breastfeeding women), but this vitamin degrades quickly with time and during cooking.
For optimal nutrient retention, it is advised to consume fresh Moringa leaves shortly after harvesting and to cook the Moringa leaves for a short time (a few minutes only), or even to eat them raw if they are young and tender
- One-half cup cooked Moringa leaves will meet your day’s need for Vitamins A and C
How to use Moringa powder?
Moringa powder can be added to soups and stews when cooking, but more nutrition is available when added at the end of cooking, or just before eating. Same apply for Moringa fresh leaves
Wondering how to consume Moringa Powder? Check out all these great Moringa Recipes
The taste of the powder is strong, so the amount that is palatable may depend upon the strength of the flavor of the soup or stew. Some flavors seem to blend well with Moringa powder (like peanut or lemon) and some don’t. Experimentation is still the best way to find out what tastes good and what doesn’t.
How to eat, use Moringa Pods?
Moringa pods are quite nutritious, and can be cooked, eaten in a variety of ways. They can be boiled, steamed, fried — essentially, eaten in any way that one might use or eat green beans or asparagus.
The pods are best for eating when they are young and tender. When they are too old, they become woody and fibrous. A good test is to bend the pod — if it snaps and breaks in half, it is good to eat. If it does not break, it is likely too old.
How to eat, use Morings Seeds?
Moringa seeds can be eaten when they are very young. When they are mature, they can be eaten, but we prefer the little baby ones. You use them as you would green peas, although you want to “go easy” when eating them, as the seeds have a remarkable ability to clean water – and likewise, a remarkable ability to clean toxins from your bloodstream. Too many at a time can be unpleasant, as the results are – a lot of waste being cleaned out fairly rapidly – and they may upset your stomach. You can “pop” the seeds like popcorn, with oil or butter, and salt, and eat them that way – but – a few at a time! Your system needs to get used to ANY new food that is introduced to it, and Moringa is one very powerful plant.
When to eat, use Moringa?
There is no specified recommendations on when to eat moringa, same like there are no recommendations on when to eat a banana.
I never heard of a recommendation to eat bananas before, during or after meals. The same goes for Moringa.
In many pages there is information, recommendations treating moringa as if it is some sort of medicine… Its not! Moringa is not a medicine, Its food. You can eat, use it with empty or full stomach. Before, during or after meals.
Moringa
A plant with multiple medicinal uses and benefits

Moringa leaf powder per day:
Calcium – 10g
• 30% of the recommended daily intake for children between 1 and 3 years old.
• 25% of the recommended daily intake for children between 4 and 9 years old as well as adult women.
• 15% of the recommended daily intake for teenagers and women over 55.
Iron – 10g
• 30% of the recommended daily intake for children between 1 and 12 years old.
• 15% of the daily recommended intake for teenagers.
• 20% of the daily recommended intake for adults over 55.
• 12% of the recommended daily intake for adult women.
• 7% of the recommended daily intake for pregnant women.
Vitamin A – 10g
• 50 to 100% of the recommended daily intake for all population categories.
How to use and eat moringa? How much moringa should you consume?
Recommendations from WHO/FAO Moringa Recommend Daily Allowances RDA